C/C++ 단일연결리스트
연결리스트의 원리
연결리스트는 배열과 다를게 요소들이 연속적이지 않음
다음과 같은 연결리스트의 종류가 있음
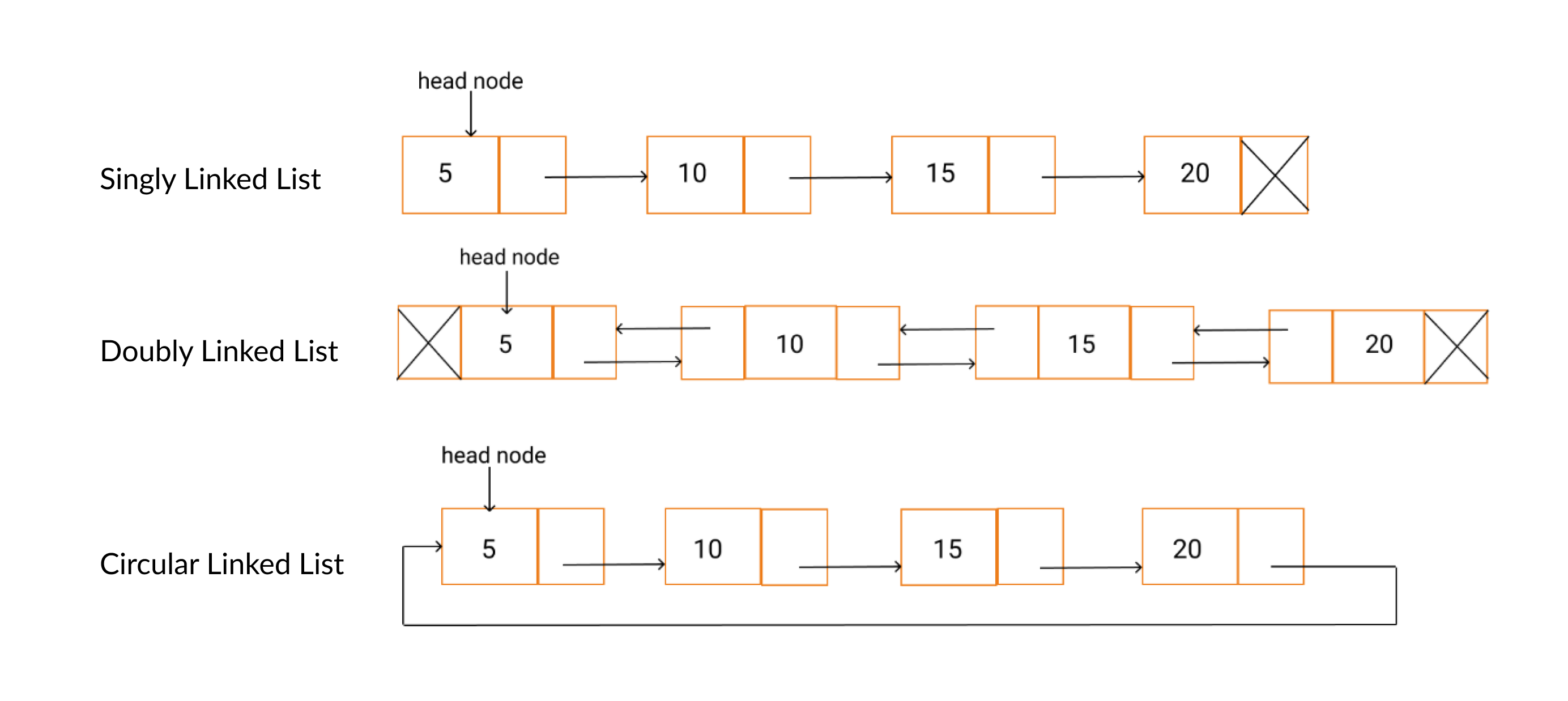
배열과 다르게 각요소가 다음 요소의 위치를 담고있는 방식으로 연결이 되어있음
배열의 장단점
장점
인덱스를 통해서 바로 접근 가능
단점
요소를 삽입, 삭제 시 요소를 이동시키는 과정이 필요함
연결리스트 장단점
장점
인덱스 대신 노드를 사용하기에 삽입 삭제가 쉽고 시간이 덜걸림
단점
리스트 처럼 인덱스로 바로 접근이 불가함
insert 기본 구현 코드
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
void Insert(int x,Node** head)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->data = x;
temp->next = NULL;
if (*head != NULL) temp->next = *head;
*head = temp;
}
void Print(Node* head)
{
cout << "List is: ";
while (head != NULL)
{
cout << " " << head->data;
head = head->next;
}
cout << "\n";
}
int main()
{
Node* head = NULL;
cout << "How many numbers\n";
int n, x;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cout << "Enter the numbers\n";
cin >> x;
Insert(x, &head);
Print(head);
}
}
리스트에 요소를 더하는 기본적인 단일 연결리스트 구현이다.
n번째에 데이터 삽입하기
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
struct Node* head;
void Print()
{
Node* temp = head;
while (temp != NULL)
{
cout << temp->data << " ";
temp = temp->next;
}
cout << "\n";
}
void Insert(int data, int n)
{
Node* temp1 = new Node;
temp1->data = data;
temp1->next = NULL;
if (n == 1)
{
temp1->next = head;
head = temp1;
return;
}
Node* temp2 = head;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 2; i++)
{
temp2 = temp2->next;
}
temp1->next = temp2->next;
temp2->next = temp1;
}
int main()
{
head = NULL;
Insert(2, 1); //List: 2
Insert(3, 2); //List: 2,3
Insert(4, 1); //List: 4,2,3
Insert(5, 2); //List: 4,5,2,3
Print();
}
n번째 요소 삭제하기
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
struct Node* head;
void Print()
{
Node* temp = head;
while (temp != NULL)
{
cout << temp->data << " ";
temp = temp->next;
}
cout << "\n";
}
void Insert(int data)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->data = data;
temp->next = NULL;
if (head != NULL) temp->next = head;
head = temp;
}
void Delete(int n)
{
Node* temp1 = head;
if (n == 1)
{
head = temp1->next;
free(temp1);
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n - 2; i++)
{
temp1 = temp1->next;
}
struct Node* temp2 = temp1->next;
temp1->next = temp2->next;
free(temp2);
}
int main()
{
head = NULL;
Insert(2);
Insert(4);
Insert(6);
Insert(5);
Print();
int n;
cout << "Enter a position\n";
cin >> n;
Delete(n);
Print();
}
단일 연결리스트
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
void printList(Node* head)
{
Node* cursor = new Node();
if (head == NULL)
cout << "Head is Null";
else
{
cout << "List is: ";
cursor = head;
while (cursor != NULL)
{
cout << cursor->data << " ";
cursor = cursor->next;
}
cout << "\n";
}
}
void insert(Node** head, int new_data, int n)
{
Node* new_node = new Node();
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = NULL;
if (n == 1)
{
new_node->next = *head;
*head = new_node;
return;
}
Node* prevN = *head;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 2; i++)
{
prevN = prevN->next;
}
new_node->next = prevN->next;
prevN->next = new_node;
}
void deleteNode(Node** head, int n)
{
Node* cursor = *head;
if (n == 1)
{
*head = cursor->next;
delete cursor;
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n - 2; i++)
{
cursor = cursor->next;
}
Node* index = new Node();
index = cursor->next;
cursor->next = index->next;
delete index;
}
int main()
{
Node* head = new Node();
head = NULL;
insert(&head, 1, 1); //List: 1
insert(&head, 4, 2); //List: 1,4
insert(&head, 5, 3); //List: 1,4,5
insert(&head, 9, 1); //List: 9,1,4,5
printList(head);
deleteNode(&head, 3);
printList(head);
return 0;
}
연결리스트 뒤집기 reverse
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
void printList(Node* head)
{
Node* cursor = new Node();
if (head == NULL)
cout << "Head is Null";
else
{
cout << "List is: ";
cursor = head;
while (cursor != NULL)
{
cout << cursor->data << " ";
cursor = cursor->next;
}
cout << "\n";
}
}
void reverse(Node** head)
{
Node* next, * prev, *current = new Node();
current = *head;
prev = NULL;
while (current != NULL)
{
next = current->next;
current->next = prev;
prev = current;
current = next;
}
*head = prev;
}
void insert(Node** head, int new_data, int n)
{
Node* new_node = new Node();
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = NULL;
if (n == 1)
{
new_node->next = *head;
*head = new_node;
return;
}
Node* prevN = *head;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 2; i++)
{
prevN = prevN->next;
}
new_node->next = prevN->next;
prevN->next = new_node;
}
void deleteNode(Node** head, int n)
{
Node* cursor = *head;
if (n == 1)
{
*head = cursor->next;
delete cursor;
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n - 2; i++)
{
cursor = cursor->next;
}
Node* index = new Node();
index = cursor->next;
cursor->next = index->next;
delete index;
}
int main()
{
Node* head = new Node();
head = NULL;
insert(&head, 1, 1); //List: 1
insert(&head, 4, 2); //List: 1,4
insert(&head, 5, 3); //List: 1,4,5
insert(&head, 9, 1); //List: 9,1,4,5
printList(head);
deleteNode(&head, 1);
printList(head);
reverse(&head);
printList(head);
return 0;
}
연결리스트에서 재귀 출력 리버스 출력 리버스를 재귀로 구현
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
void printList(Node* p)
{
if (p == NULL)
{
cout << '\n';
return;
}
cout << p->data << " ";
printList(p->next);
}
void reverse_printList(Node* p)
{
if (p == NULL)
{
return;
}
reverse_printList(p->next);
cout << p->data << " ";
}
void reverse(Node** head,Node *p)
{
if (p->next == NULL)
{
*head = p;
return;
}
reverse(head ,p->next);
Node* next = p->next;
next->next = p;
p->next = NULL;
}
void insert(Node** head, int new_data, int n)
{
Node* new_node = new Node();
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = NULL;
if (n == 1)
{
new_node->next = *head;
*head = new_node;
return;
}
Node* prevN = *head;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 2; i++)
{
prevN = prevN->next;
}
new_node->next = prevN->next;
prevN->next = new_node;
}
void deleteNode(Node** head, int n)
{
Node* cursor = *head;
if (n == 1)
{
*head = cursor->next;
delete cursor;
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n - 2; i++)
{
cursor = cursor->next;
}
Node* index = new Node();
index = cursor->next;
cursor->next = index->next;
delete index;
}
int main()
{
Node* head = new Node();
head = NULL;
insert(&head, 1, 1); //List: 1
insert(&head, 4, 2); //List: 1,4
insert(&head, 5, 3); //List: 1,4,5
insert(&head, 9, 1); //List: 9,1,4,5
printList(head);
deleteNode(&head, 1);
printList(head);
reverse(&head,head);
printList(head);
reverse_printList(head);
/* 총 출력
* 9 1 4 5
1 4 5
5 4 1
1 4 5
*/
return 0;
}

Leave a comment